Objective
to determine whether the benefits of QFR guidance persist at 2 years, particularly for patients in whom QFR changed the revascularisation strategy
Study
multicentre, blinded, randomized, sham-controlled clinical trial
Population
patients over 18 with ACS or CCS and and one lesion with a diameter stenosis of 50-90% in a coronary artery with reference vessel diameter of at least 2.5 mm
Endpoints
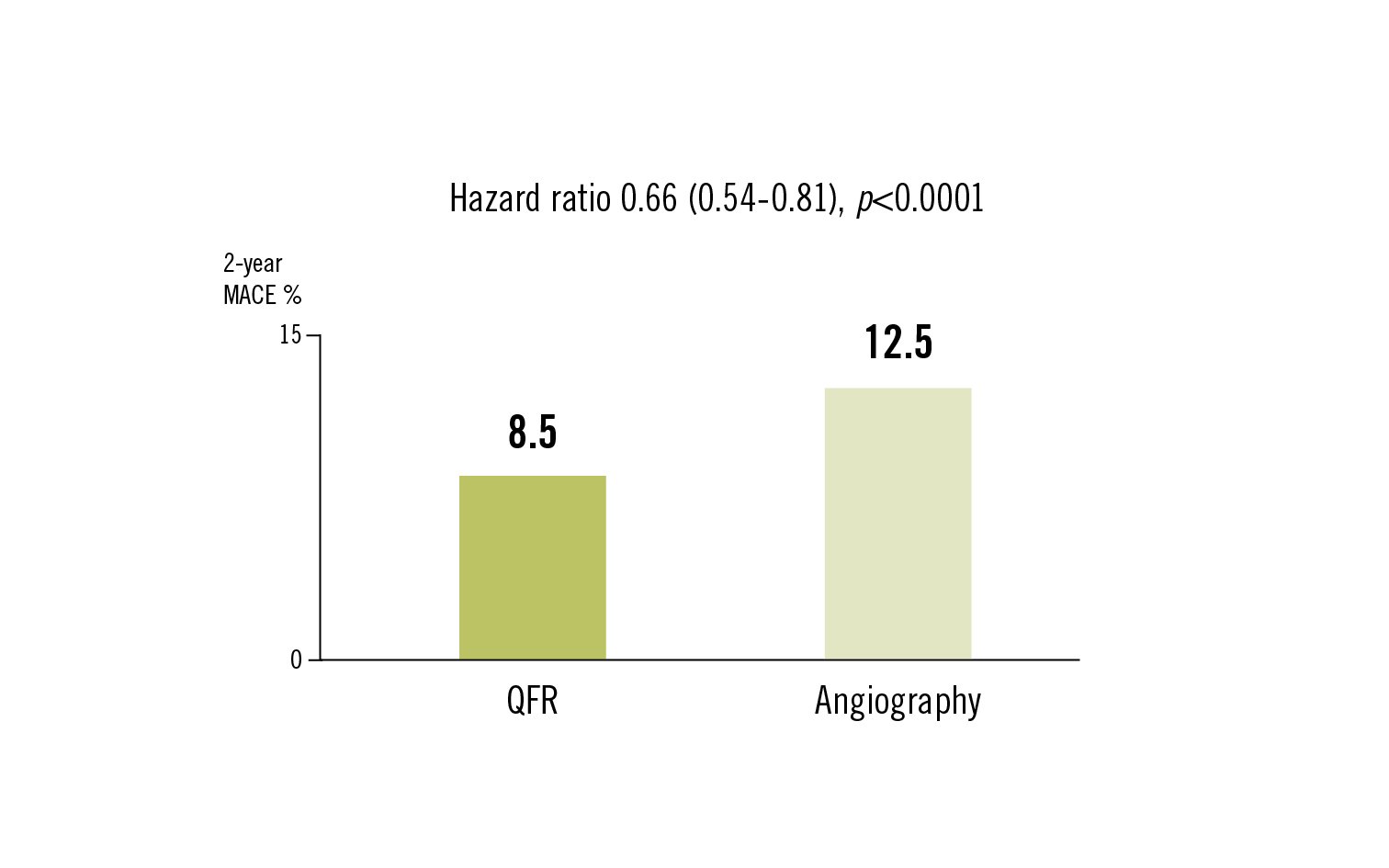
MACE (all-cause death, myocardial infarction, ischaemia-driven revascularisation)
Conclusion
QFR-guided lesion selection improved 2-year clinical outcomes compared with standard angiographic guidance. The benefits were most pronounced among patients in whom QFR assessment altered the planned revascularisation strategy
Song et al. J Am Coll Cardiol.2022;80:2089-101