Objective
to assess the safety and efficacy of clopidogrel compared with ticagrelor or prasugrel in older patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome (NSTE-ACS)
Study
open-label, randomised controlled trial 1:1 ratio
Population
patients aged 70 years or older with NSTE-ACS
Endpoints
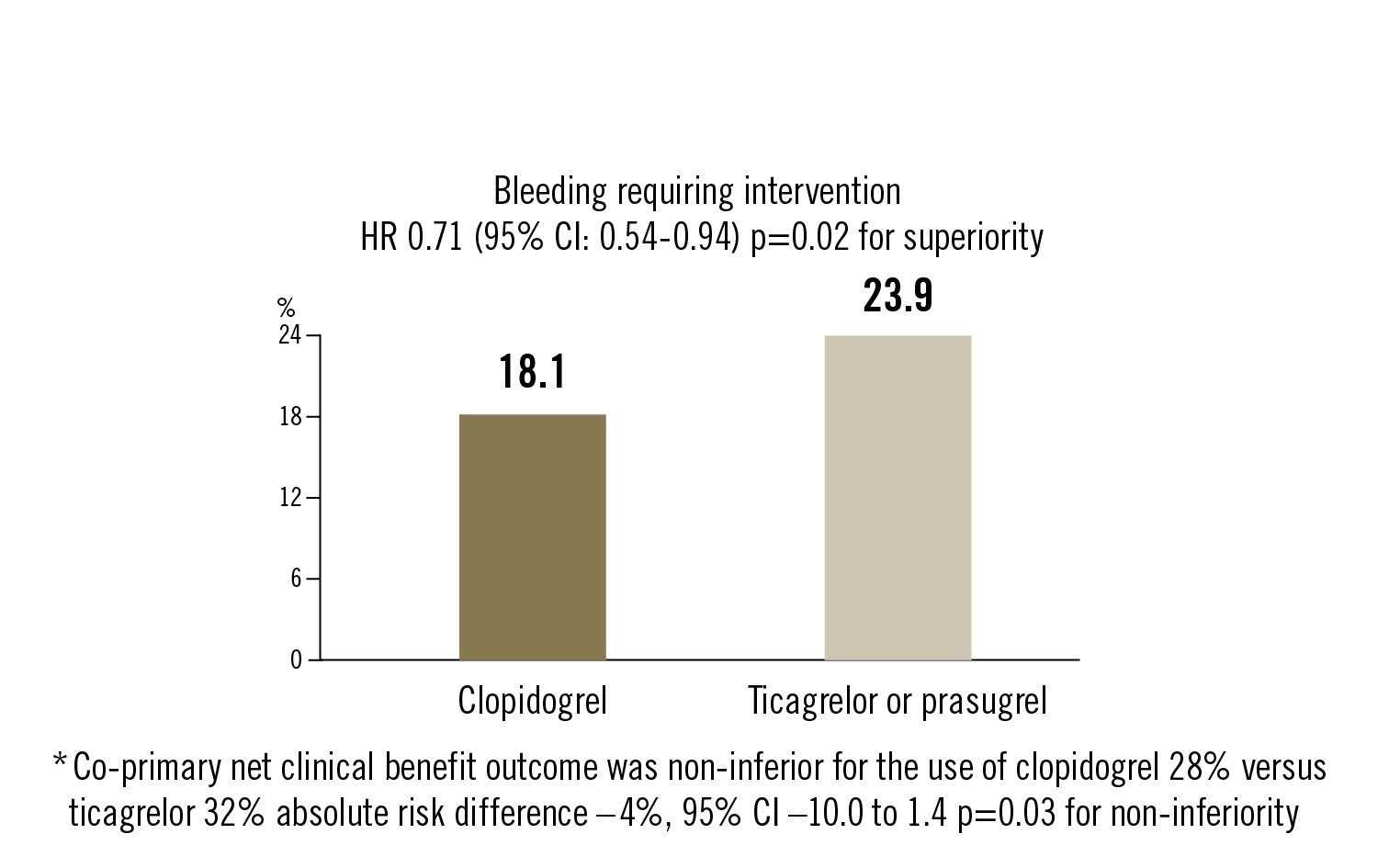
First primary outcome bleeding requiring intervention, defined by PLATelet inhibition and patient Outcomes (PLATO) major or minor bleeding. Co-primary outcome of all-cause death, MI, stroke, PLATO major or minor bleeding. All at 12 months.
Conclusion
in patients aged 70 years or older presenting with NSTE-ACS, clopidogrel is a favourable alternative to ticagrelor, because it leads to fewer bleeding events without an increase in the combined endpoint of all-cause death, MI, stroke or bleeding
Gimbel et al. Lancet. 2020;395:1374-81