Objective
to investigate whether remote ischaemic pre-conditioning (RIPC) conducted 24 hours before PCI or CAG could reduce the occurrence of contrast-associated acute kidney injury (CA-AKI)
Study
prospective double-blind randomised sham-controlled trial
Population
patients at risk of acute kidney injury (Mehran Score 6)
Endpoints
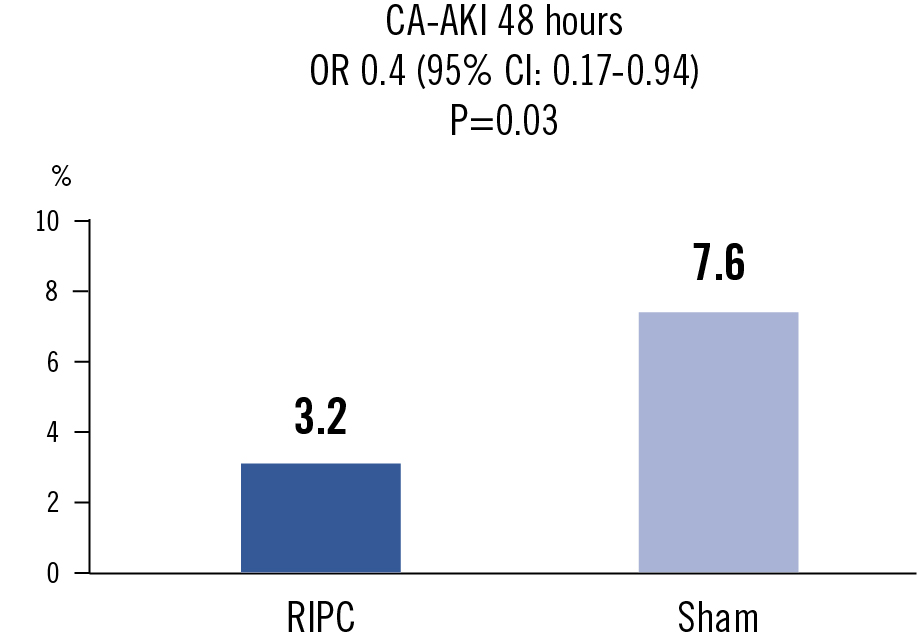
the occurrence of CA-AKI, defined as an increase in serum creatinine of 0.3mg/dL (26.5 mmol/L) from baseline within 48 hours after CAG or PCI
Conclusion
Among patients at high risk of acute kidney injury undergoing CAG or PCI, delayed RIPC reduces the incidence of CA-AKI compared to sham.
Jia et al. Eur Heart J. 2025 Mar 11:ehaf135.